Summary
|
|
What is NMN?
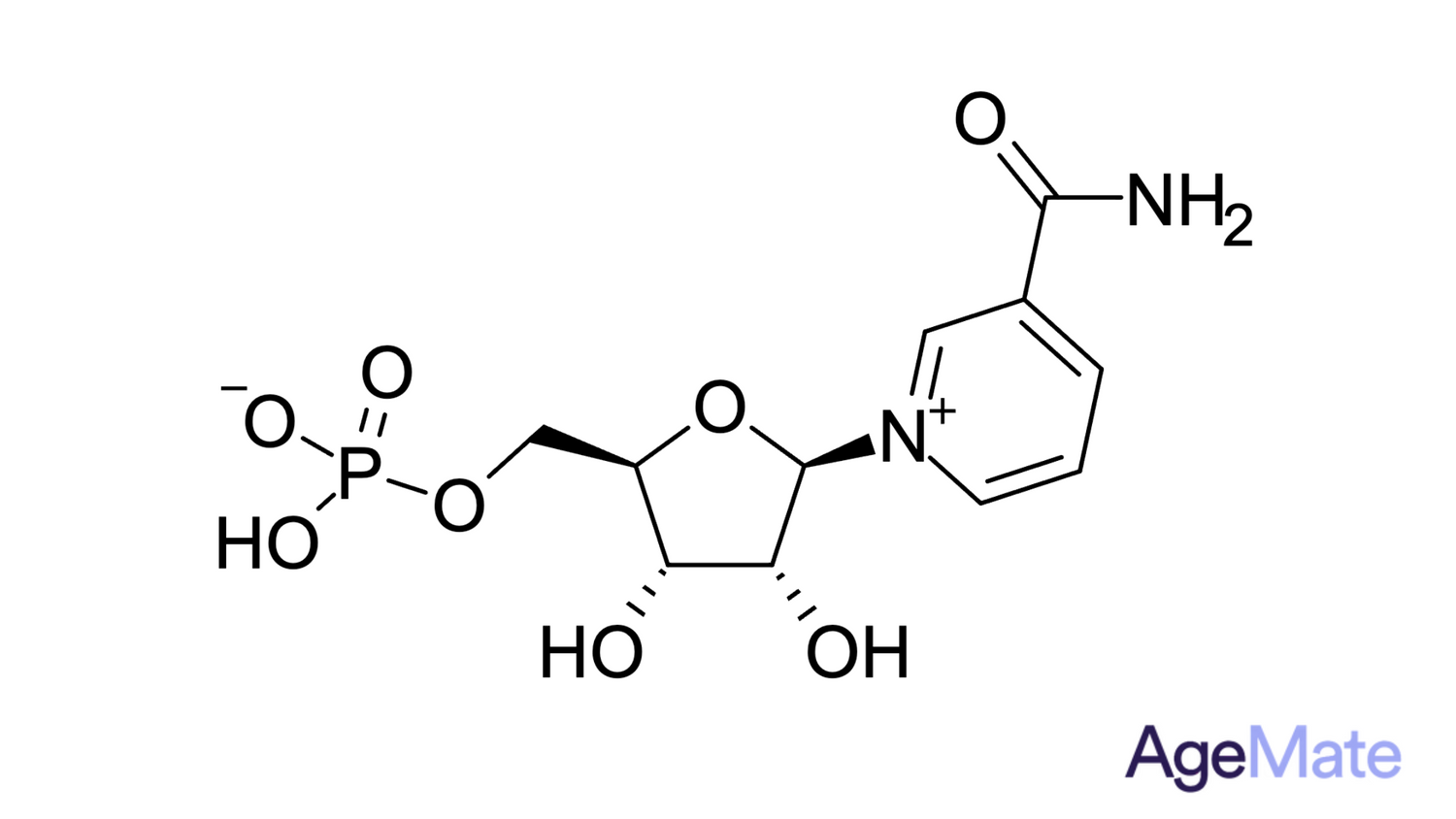
NMN is a naturally occurring compound present in fruits, milk, and vegetables. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) is a compound that plays a crucial role in cellular energy production.
It serves as a precursor to Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+), a coenzyme that is integral for various biological functions within the body. NAD+ is involved in processes like DNA repair, energy metabolism, and maintaining cellular health.
NMN Impact on Ageing
NMN maintains mitochondrial health by boosting NAD+, aiding energy production, and preserving cellular vitality amidst age-related declines (R).
Aging reduces NAD+, affecting stem cells. NMN restores NAD+ (R), possibly preserving stem cell activity crucial for tissue repair (R).
NMN affects gene expression via epigenetic mechanisms, potentially maintaining cellular integrity by supporting NAD+ production during aging (R).
NAD+ aids intercellular signalling. NMN's role in NAD+ production supports effective cell communication, potentially sustaining vital cellular functions for healthy aging (R).
NAD+ affects nutrient sensing. NMN boosts NAD+, potentially regulating nutrient sensing, optimising metabolism, and possibly countering age-related metabolic imbalances (R).
NAD+ influences cellular "clean-up" processes like macroautophagy. NMN's NAD+ support aids efficient cellular maintenance, potentially fighting age-related cellular damage buildup (R).
Preserving NAD+ levels through NMN supplementation may help in preserving DNA repair mechanisms, reducing genomic instability, and supporting cellular integrity against age-related DNA damage (R).
NMN and Longevity Studies
Studies exploring the effects of NMN on longevity and healthier aging have shown promising results, in both animal and human models (R).
Animal studies have demonstrated that supplementation with NMN can improve various markers associated with aging including enhanced metabolism, improved mitochondrial function, and extension of lifespan (R, R).
Studies suggest NMN's link to improved metabolism, impacting glucose and lipid utilisation (R). NMN increased muscle insulin sensitivity, insulin signalling, and remodelling in prediabetic women (R).
NMN prevented aging-related muscle dysfunctions and improved physical performance (R, R, R, R)
In some animal studies, NMN supplementation has been associated with increased longevity, where treated groups showed a prolonged lifespan compared to control groups (R).
In human studies, NMN was linked to increased telomere length (R).

The fluctuations in NAD+ levels with age (a), methods to replenish NAD+ levels (b), and the wellness advantages of replenishing NAD+ through NMN supplementation (c). Image Source: Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of American Society for Nutrition.
Research indicates that elevated NAD+ levels, facilitated by NMN supplementation, can enhance sirtuin activity (R).