Summary
|
|
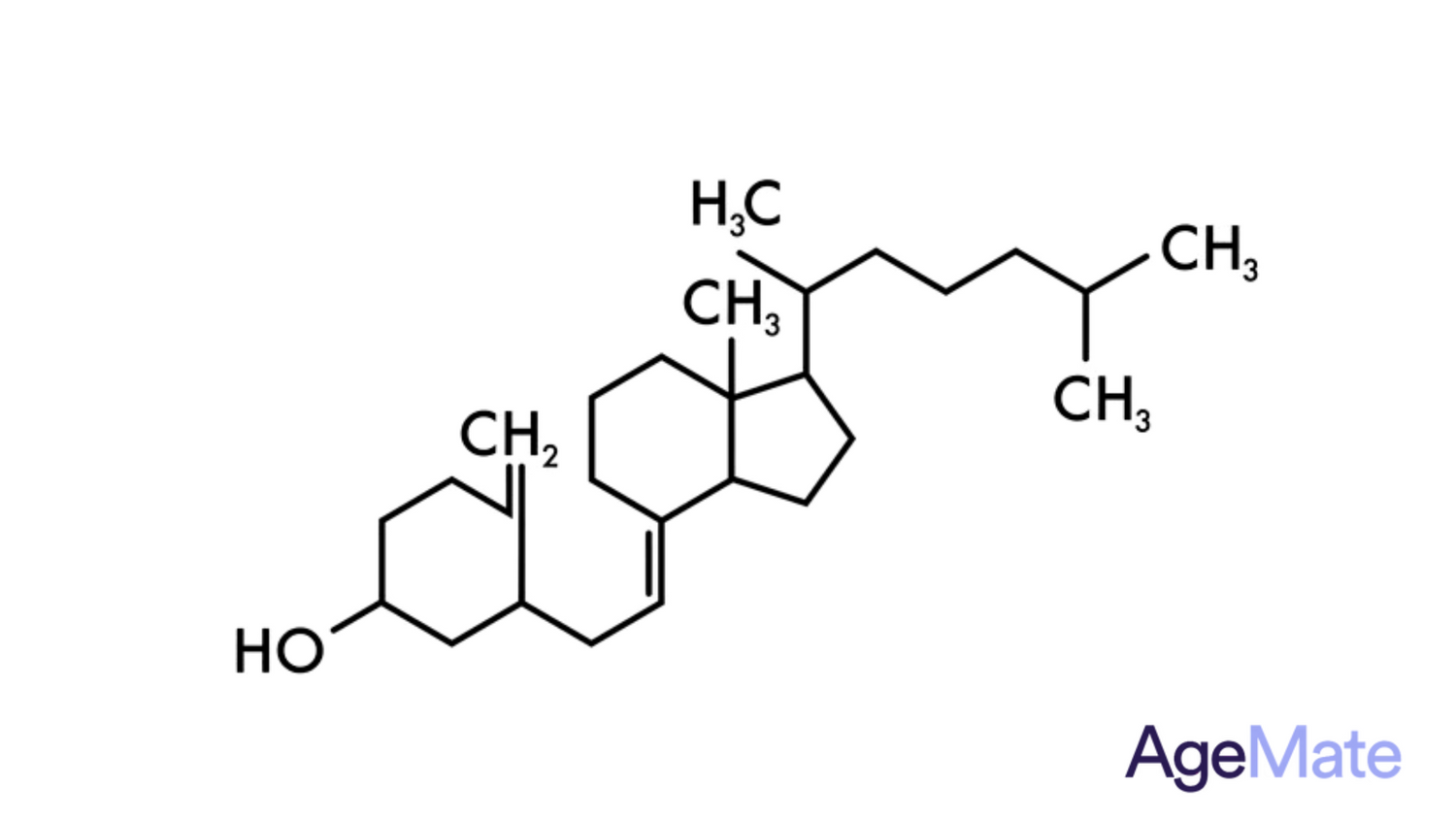
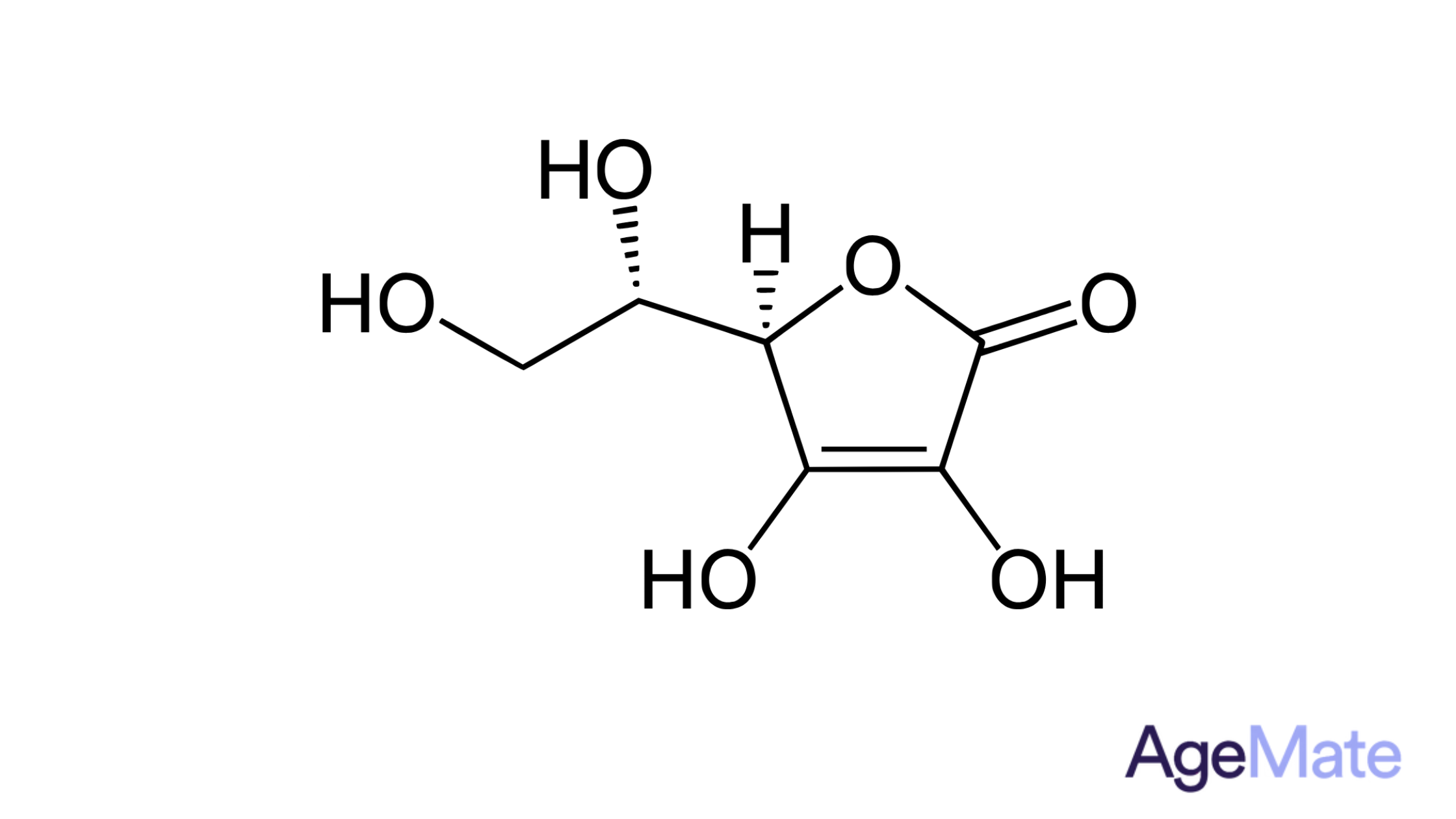
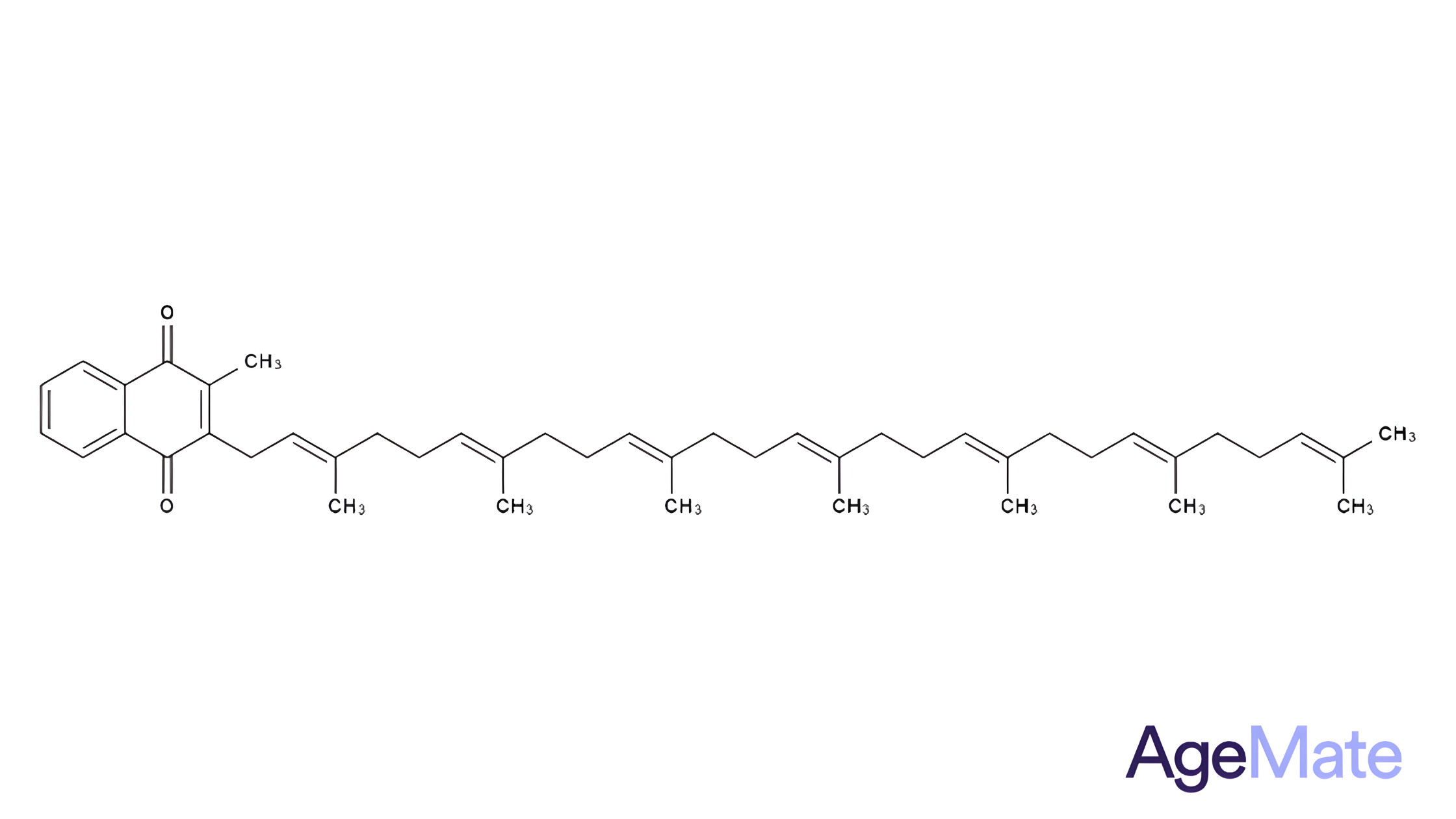
What is Vitamin D3?
Vitamin D3 is essential for strong bones and teeth, aiding calcium absorption. It's obtained from sunlight, certain foods, and supplements. Deficiency can weaken bones and impact overall health, potentially affecting muscles and increasing fracture risk. Maintaining adequate levels through diet, sunlight, and supplements is crucial for optimal health (R).
Vitamin D3 Impact on Aging
Vitamin D3 plays a significant role in aging-related health. As people age, their ability to produce and absorb vitamin D3 decreases, potentially leading to deficiencies (R).
Adequate levels of vitamin D3 are crucial for maintaining bone health, reducing the risk of fractures, and preventing conditions like osteoporosis, which become more prevalent with age (R).
Vitamin D3 is believed to support muscle strength, which is crucial in preventing falls, a common concern among the elderly (R, R).
Some research also suggests a potential role in reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, certain cancers, and cognitive decline. However, more studies are needed to confirm these effects definitively (R).
Vitamin D3 and Longevity Studies
Studying 18 randomised controlled trials with 57,311 participants, researchers discovered that vitamin D supplementation correlated with a 7% decrease in overall mortality (R).
Studies show vitamin D metabolism is similar in nematodes and mammals. It prevents the build-up of certain proteins linked to aging and promotes longer life by supporting protein balance through specific pathways involving IRE-1, XBP-1, and SKN-1 (R).

Image Sourced: Cell Reports. Vitamin D supplementation in C. elegans slows aging by maintaining protein balance, revealing a new aspect of how Vitamin D influences aging (R).
The CHANCES Consortium is a large-scale study involving European cohorts. It examined the association between vitamin D3 levels and mortality. It found that higher levels of vitamin D3 were associated with a reduced risk of mortality from all causes (R, R).
A Study in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition investigated the relationship between serum vitamin D3 levels and mortality in older adults. It suggested an inverse association between higher vitamin D3 levels and mortality risk (R).
The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) often studied vitamin D3 levels and mortality causes. Some findings linked low vitamin D3 levels to higher mortality from heart diseases and cancer (R).
A Meta-analysis in the British Medical Journal (BMJ) examined various studies on vitamin D3 supplementation and mortality. It concluded that vitamin D3 supplementation might be associated with a decrease in mortality from all causes (R).
The VITAL trial studied the effects of vitamin D3 supplementation on cancer and heart disease. It hinted at a slight decrease in overall mortality in those who took vitamin D3 compared to the placebo group (R).