Summary
|
|
What is Vitamin C?
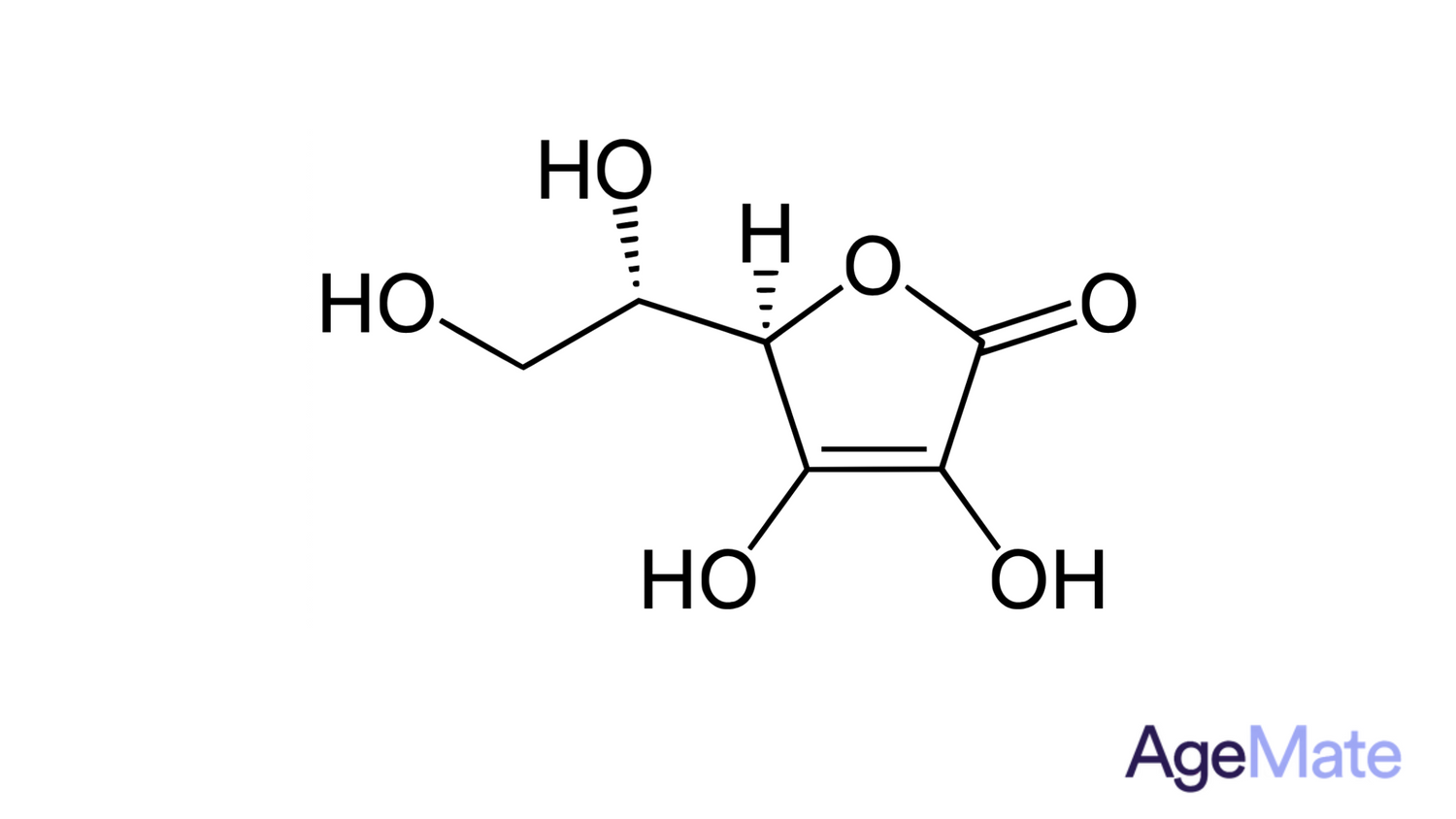
Vitamin C, also called ascorbic acid, is a crucial water-soluble vitamin that can't be produced by the body and must be obtained from diet or supplements. Known for its antioxidant properties, it protects cells from damage and supports collagen production, immune function, and wound healing. Sources of Vitamin C include citrus fruits, berries, bell peppers, broccoli, and supplements.
Vitamin C Impact on Aging
Studies have indicated that Vitamin C plays a crucial role in combating cellular damage caused by oxidative stress, a key contributor to aging (R, R, R).
Its antioxidant properties may help reduce the impact of free radicals, potentially slowing down age-related degeneration in cells and tissues (R).
The "sink hypothesis (R)" suggests vitamin C's potential in promoting healthy brain aging (R).
Vitamin C's involvement in collagen production can contribute to skin elasticity, possibly delaying visible signs of aging, such as wrinkles and fine lines (R).
The visible effects of aging on the skin can be improved by supplementing with vitamin C. Several studies support this claim (R).
Image Sourced: Nutrients. Vitamin C and other antioxidants play a crucial role in skin health. The cooperation between vitamins E and C and glutathione in neutralising free radicals and restoring antioxidants is evident. Vitamin E resides in the cell's lipid portion, while vitamin C and glutathione are water-soluble and found in the cytosol.
Vitamin C and Longevity Studies
By scavenging free radicals, vitamin C can potentially reduce cellular damage and support healthier aging (R).
Research suggests that adequate levels of vitamin C in the body may decrease oxidative stress, which plays a role in aging-related diseases and the aging process itself. Reducing oxidative stress might positively influence lifespan and age-related health issues (R).
The findings of this study indicate a positive relationship between the intake of vitamin C and the length of human telomeres (R).
While vitamin C isn't a direct longevity booster, its ability to mitigate cellular damage might indirectly affect aging. It's often seen as part of a broader strategy for healthy aging rather than a singular anti-aging solution (R).
Long-term observational studies have indicated that diets rich in fruits and vegetables, primary sources of vitamin C, are linked to better health outcomes and potentially longer lifespans. This correlation reinforces the importance of vitamin C in a balanced diet for overall health (R, R).
Studies have highlighted various health benefits of vitamin C, such as improved immune function, collagen synthesis for skin health, and enhanced iron absorption. These factors indirectly contribute to overall well-being, potentially impacting longevity (R).
Observational studies have suggested that individuals with higher Vitamin C levels in their diet or bloodstream tend to exhibit better overall health and a lower risk of age-related diseases (R, R).