Inflammation, the body's intricate and finely tuned defence mechanism, is a double-edged sword in human physiology. It's a powerful and essential response, a biological defender poised to protect you from infections, injuries, and other threats. Yet, like any hero, it can become a formidable adversary when things go awry, causing chronic diseases and tissue damage. In this dynamic interplay of defence and disorder, understanding the intricate nature of inflammation becomes paramount in our quest for health and well-being (R).
Let's explore this interplay.
What is inflammation?
Inflammation in human physiology is a complex and vital biological response to injury, infection, or tissue damage. It's a natural defence mechanism that helps the body protect itself and promote healing. Where it can all go wrong is when chronic inflammation rears its head.
What is chronic inflammation?
Chronic inflammation in human physiology refers to a long-lasting and persistent inflammatory response that continues for weeks, months, or even years. Unlike acute inflammation, which is a short-term and beneficial response to injury or infection, chronic inflammation is characterised by a sustained and often dysregulated immune reaction. It can occur throughout the body and is associated with various diseases and health conditions (R, R).
What does chronic inflammation do to the body?
Chronic inflammation can have a profound and detrimental impact on the body, contributing to various health problems and increasing the risk of various diseases. Here are some of the effects of chronic inflammation on the body:
Tissue Damage: It can lead to persistent tissue damage and scarring over time. This damage can impair the normal functioning of organs and tissues, potentially leading to chronic pain and decreased organ function (R).
Cardiovascular Disease: Chronic inflammation plays a central role in the development and progression of cardiovascular diseases, including atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), which can lead to heart attacks and strokes (R).
Diabetes: It can interfere with the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels and contribute to insulin resistance, a hallmark of type 2 diabetes (R).
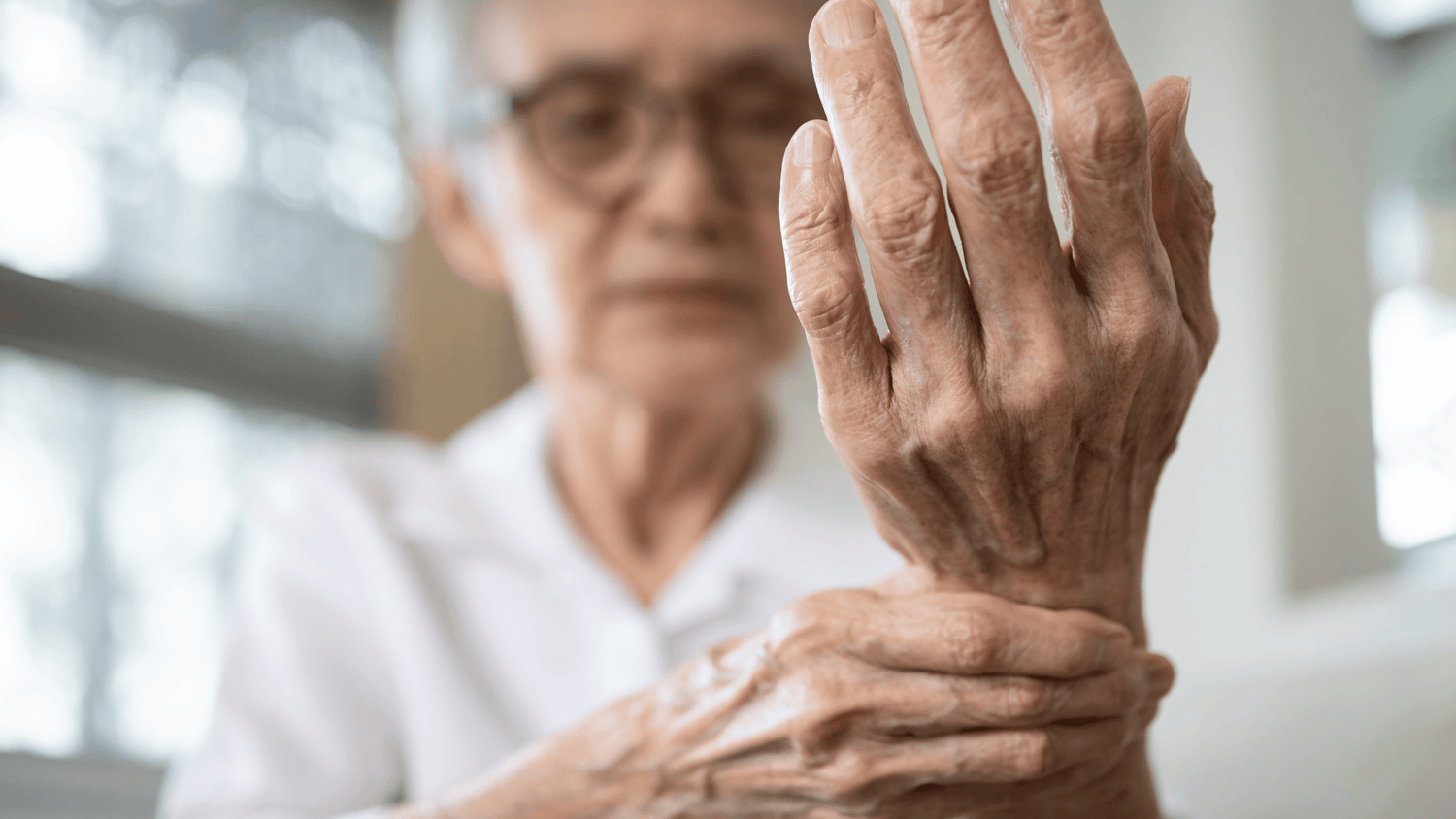
Autoimmune Disorders: In autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues, leading to chronic inflammation and tissue damage (R).
Neurodegenerative Diseases: There is growing evidence linking it to neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. Inflammation may contribute to the progression of these conditions (R, R).
Obesity: Excessive adipose (fat) tissue can produce inflammatory substances. In obesity it contributes to insulin resistance, cardiovascular problems, and other obesity-related complications (R).
Cancer: It has been associated with an increased risk of certain cancers. Inflammatory processes can promote the growth and spread of cancer cells (R).
Digestive Disorders: Chronic digestive tract inflammation is a hallmark of conditions like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. These conditions can cause pain, diarrhoea, and damage to the digestive system (R).
Respiratory Conditions: In the airways it can contribute to conditions such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (R).
Joint Pain: Chronic joint inflammation is a key feature of arthritis, leading to pain, swelling, and joint damage (R).
Skin Conditions: Inflammation is involved in various skin disorders, including psoriasis and eczema (R).
Mental Health: Emerging research suggests that it may play a role in mood disorders like depression and anxiety (R).
It's important to note that chronic inflammation can be silent, meaning individuals may not experience obvious symptoms. Regular health check-ups and monitoring of inflammatory markers can help detect without symptoms.
Why it's essential to reduce inflammation for longevity
Reducing inflammation is crucial for longevity due to its profound impact on overall health. Here's why it matters:
Preventing Chronic Diseases: As identified above, chronic inflammation is closely linked to various serious diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and neurodegenerative conditions. Mitigating it reduces the risk of these life-threatening illnesses (R).
Preserving Organ Function: It can lead to tissue damage and scarring, impairing the normal functioning of vital organs. Reducing inflammation helps maintain organ health and function, ensuring they perform optimally for years to come (R).
Enhancing Immune Function: It weakens the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections and diseases. By keeping inflammation in check, you bolster your immune system, which is essential for a long and healthy life (R, R).
Improving Mental Health: Emerging research suggests a link between chronic inflammation and mood disorders like depression and anxiety. Reducing it can positively impact mental well-being, promoting a happier and more fulfilling life (R).
Supporting Healthy Weight Management: Chronic inflammation is associated with obesity-related complications and insulin resistance. By reducing, you support healthy weight management, reducing the risk of obesity-related diseases (R).
Optimising Joint and Muscle Health: In joints it leads to conditions like arthritis and chronic pain. Reducing inflammation helps preserve joint and muscle health, ensuring mobility and vitality in later years (R).
Promoting Cardiovascular Health: It is central to cardiovascular diseases like atherosclerosis. Reducing inflammation protects your heart and blood vessels, potentially adding years to your life (R).
Increasing Energy and Vitality: Chronic inflammation can sap energy and vitality. Lowering inflammation levels can lead to increased energy and a higher quality of life as you age (R).
Slowing the Aging Process: It is a key driver of cellular aging. By reducing it, you can slow down the aging process at a cellular level, potentially extending your lifespan (R).
Enhancing Quality of Life: Ultimately, reducing improves quality of life. It allows you to enjoy your later years with fewer health challenges and greater well-being (R).
Incorporating anti-inflammatory strategies into your lifestyle, such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and avoiding harmful habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, can significantly reduce inflammation and enhance longevity. But, let’s learn more about that.
What can I do to reduce the risk of chronic inflammation?
Reducing the risk of chronic inflammation involves adopting a healthy lifestyle and making choices that support overall well-being. Here are some strategies to help mitigate the risk:
Maintain a Balanced Diet:
- Emphasise whole, unprocessed foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Incorporate anti-inflammatory foods such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), nuts (especially walnuts), seeds (flaxseeds, chia seeds), and spices (turmeric, ginger).
- Minimise or avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and foods high in refined carbohydrates.
- Limit or eliminate trans and saturated fats in fried foods, baked goods, and red meat (R).
Follow a Mediterranean diet:
- Olive oil is the main fat, cereal products, legumes, fruit and vegetables, moderate fish intake, low in dairy and meat products, and moderate wine consumption (R).
Limit Processed Meats:
- Reduce consumption of processed meats like bacon, sausages, and deli meats, as they may contain additives and preservatives associated with inflammation (R, R).
Anti-Inflammatory Supplements:
- Consider incorporating supplements with anti-inflammatory properties, such as omega-3 fatty acids, curcumin (from turmeric), or green tea extract. Consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements (R).
Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
- Include sources of omega-3 fatty acids in your diet, such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. Omega-3s have anti-inflammatory properties (R).
Probiotics:
- Consider incorporating probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, and fermented foods into your diet to promote a healthy gut microbiome (R, R).
Regular Physical Activity:
- Regular exercise, including aerobic activities like walking, jogging, cycling, and strength training.
- Exercise helps reduce, improve circulation, and support overall health (R).
Manage Stress:
- Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or mindfulness.
- Chronic stress can contribute, so finding effective stress management strategies is essential (R).
Adequate Sleep:
- Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Sleep is crucial for reducing inflammation and promoting overall health (R).
Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- If overweight, losing excess weight through a balanced diet and exercise can help, particularly in adipose tissue (R).
Limit Alcohol Intake:
- Consume alcohol in moderation or avoid it altogether (R).
Avoid Smoking:
- Smoking significantly contributes to chronic inflammation and is associated with numerous health risks. Quitting smoking is a significant step toward reducing (R).
Stay Hydrated:
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day to support overall bodily functions, including immune system health (R).
Regular Health Check-Ups:
- Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your health and assess inflammatory markers if necessary.
Remember that individual responses to lifestyle changes can vary, and it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian before making significant dietary or lifestyle changes.
Conclusion
Chronic inflammation, an enduring immune response, poses substantial health risks, but proactive choices can counter its impact. A balanced diet featuring anti-inflammatory foods and regular exercise promotes wellness. Stress management techniques, ample sleep, and healthy weight further reduce inflammation. Restraining alcohol consumption and quitting smoking are crucial steps. Staying hydrated and periodic health check-ups are also vital. Anti-inflammatory supplements and probiotics can supplement these efforts. These strategies empower and safeguard your health. By prioritising well-being, you will journey towards vitality, longevity, and triumph over chronic inflammation's adverse effects.