Summary
|
|
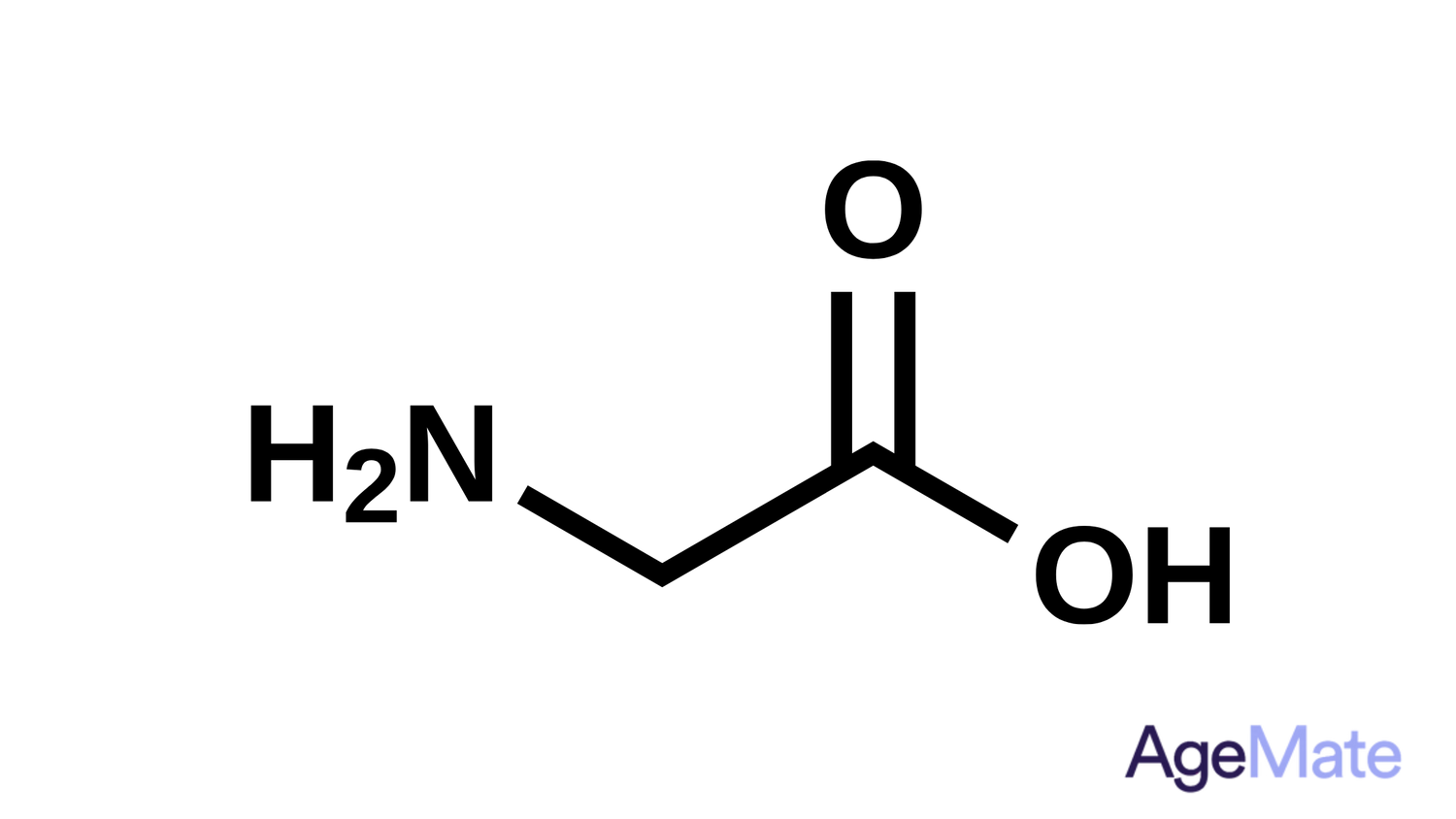
What is Glycine?
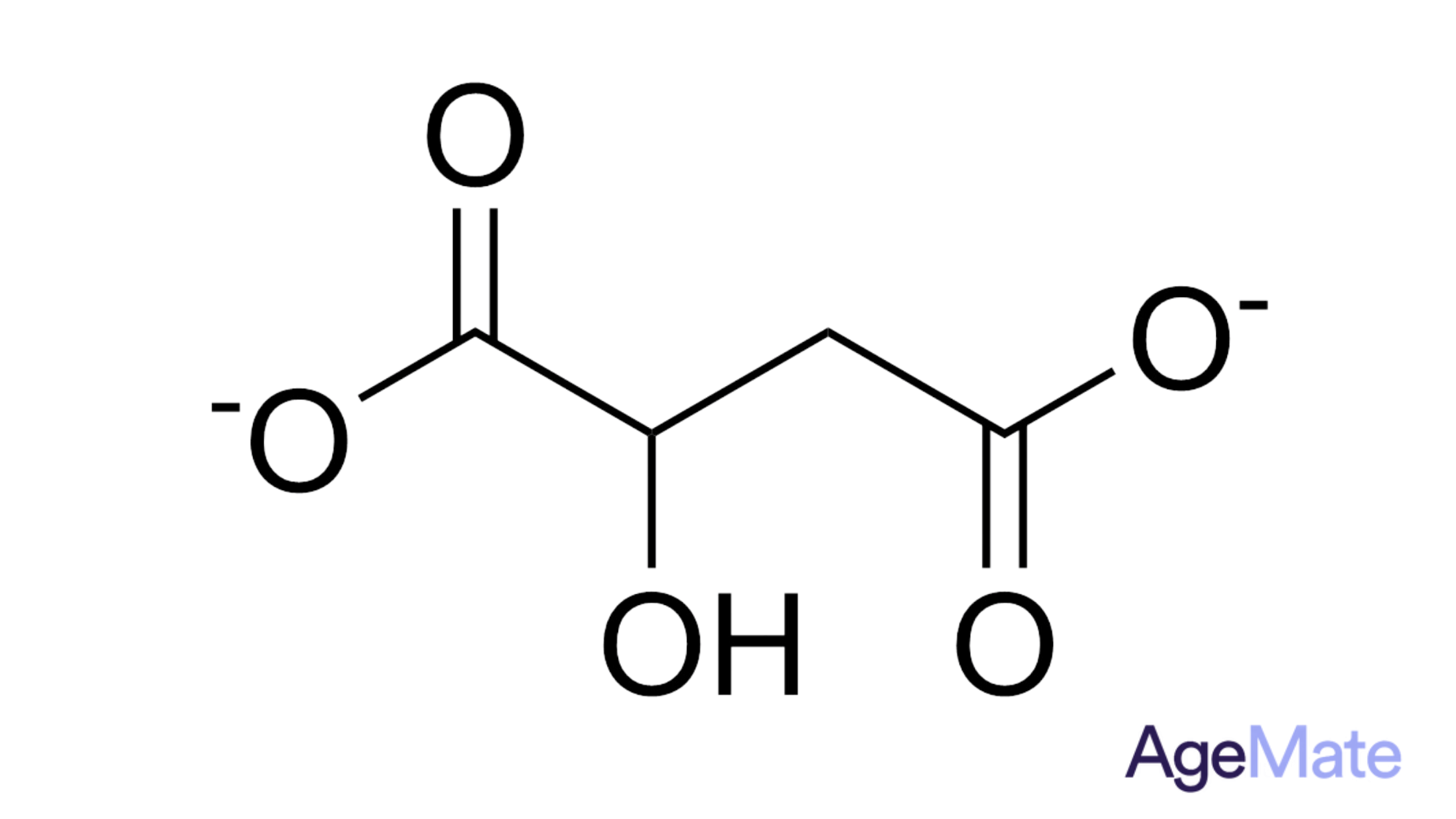
Glycine is a vital amino acid that builds proteins and contributes to various bodily functions. It's both naturally produced in the body and obtained from protein-rich foods. Besides protein synthesis, glycine acts as a neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, potentially influencing relaxation, sleep, and cognitive processes.
Glycine Impact on Aging
As an amino acid, glycine contributes to protein synthesis, aiding tissue repair and maintenance, which can be crucial for addressing age-related changes (R).
Glycine's involvement as a neurotransmitter in the central nervous system may have implications for cognitive health and sleep patterns, which can be affected by aging (R, R).
Glycine contributes to healthy mitochondria, the cellular powerhouses crucial for energy production. It supports methionine metabolism, which is essential for proper methylation and is linked to healthy aging processes (R).
This research suggests glycine treatment can counteract aging-related mitochondrial issues (R).
Glycine's antioxidant properties might help counteract oxidative stress linked to aging and age-related diseases (R, R).
Glycine and Longevity Studies
Research on glycine's impact on longevity indicates promising outcomes across various organisms.
Studies have shown that glycine supplementation extends lifespan in fruit flies (R) and the C. elegans worm (R). These findings suggest that glycine plays a significant role in promoting longevity.
Glycine levels in C. elegans varied across life stages. Supplementing glycine from larval development through adulthood extended lifespan significantly. Early or lifelong intake increased lifespan, while larval-stage supplementation showed no effect. Reducing mel-32 notably boosted lifespan, indicating its role in glycine-related longevity. Image sourced: PLOS Genetics.
Limiting methionine seems to be an evolutionary tactic for slowing aging. In rodents, supplementing with glycine has displayed potential to imitate this restriction, thus prolonging lifespan (R).
Glycine, as an antioxidant and a chaperone, safeguards proteins and assists in their proper recycling, which is crucial for maintaining cellular health as we age and reducing oxidative stress (R).
In rodents, glycine aids cells in resisting the adverse effects of excessive glycation, another aspect linked to aging (R).