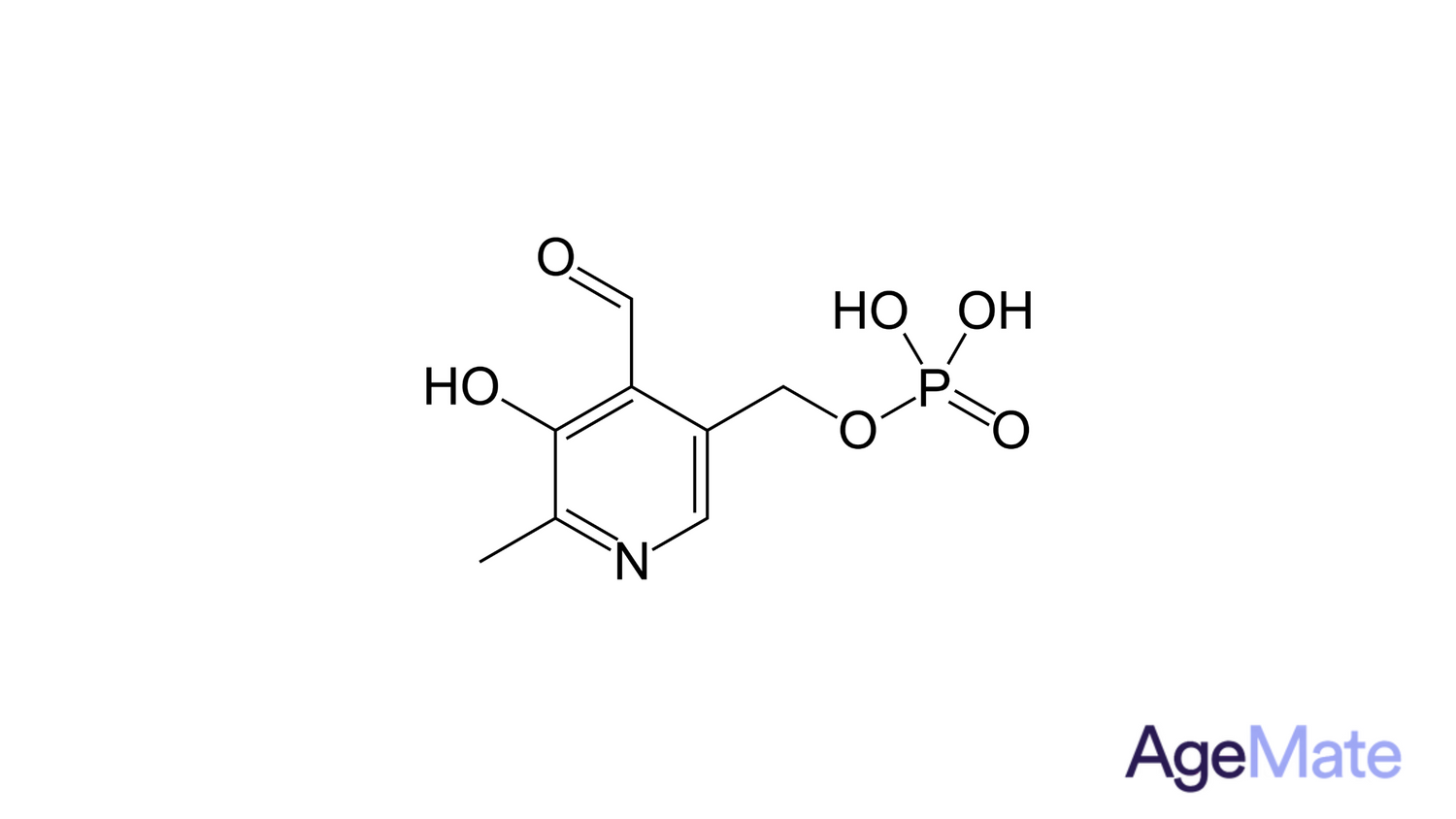
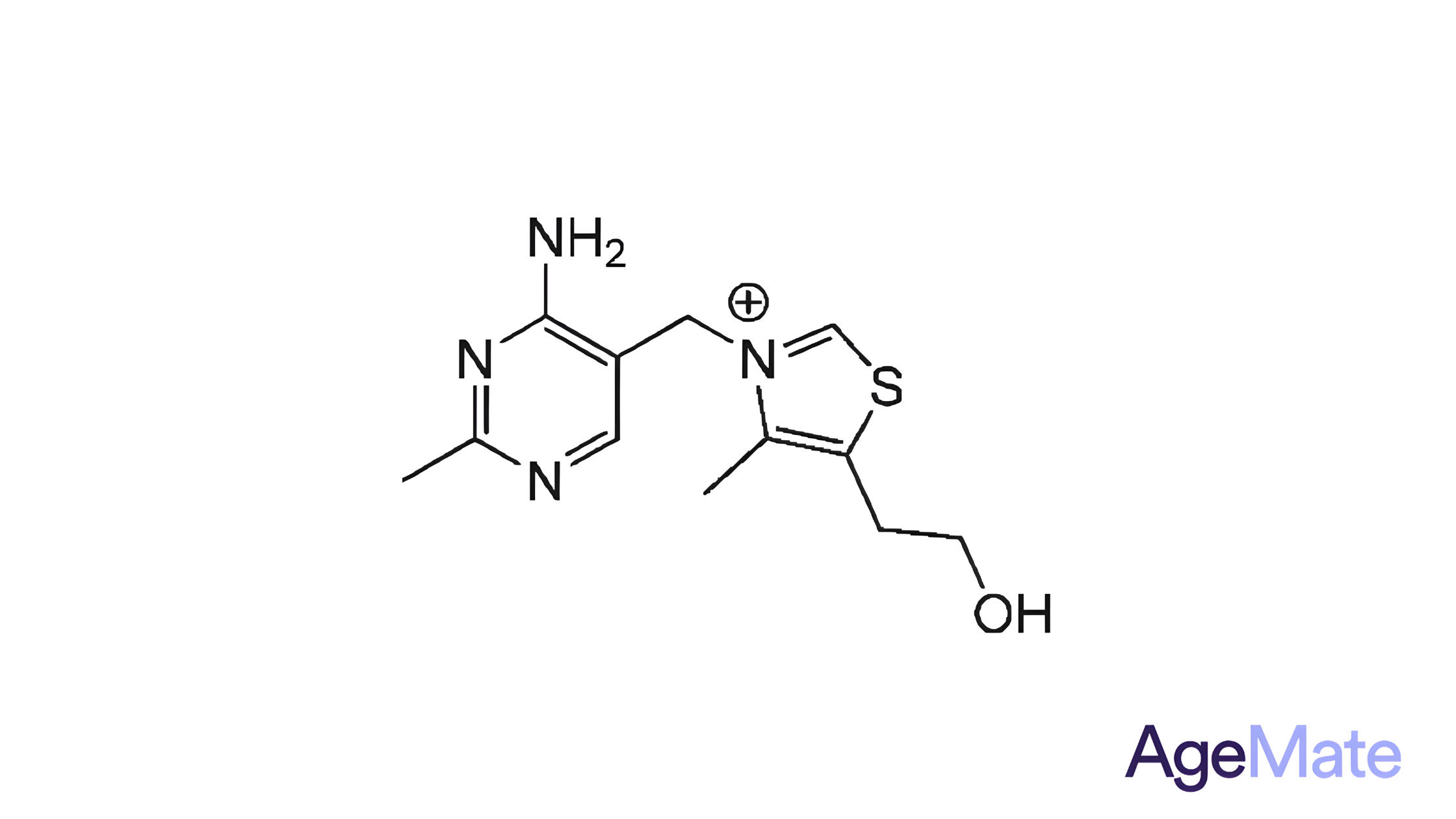
What is Pyridoxine HCI and Pyridoxal 5'-Phosphate?
Pyridoxine HCl and Pyridoxal 5'-Phosphate (PLP) are two forms of Vitamin B6, an essential nutrient that plays a vital role in various physiological functions.
Pyridoxine HCl (Hydrochloride)
This is the hydrochloride salt form of Pyridoxine, one of the most commonly used forms of Vitamin B6 in dietary supplements. Pyridoxine is necessary to properly function sugars, fats, and proteins in the body. It is also crucial for the growth and development of the brain, nerves, skin, and many other parts of the body. The hydrochloride form is water-soluble and can be taken orally to prevent or treat low levels of Vitamin B6.
Pyridoxal 5'-Phosphate (PLP)
PLP is the active form of Vitamin B6 inside the body. It is a coenzyme in many enzyme reactions, primarily in amino acid metabolism, including neurotransmitter synthesis (such as serotonin and dopamine), histamine synthesis, and hemoglobin production and function.
PLP is involved in more than 100 enzyme reactions, most of which are related to protein metabolism. It can also influence mood, cognitive function, and immune response. Supplements containing PLP are often considered more bioavailable or "active" because the body does not need to convert them into an active form.
Pyridoxine HCI and Pyridoxal 5'-Phosphate Impact on Aging and Longevity
Supplementation with pyridoxine HCl significantly improved lymphocyte responsiveness and immunocompetence in older adults, suggesting that improving vitamin B6 status is vital for stimulating immune competence in older age groups (R).
PLP plays a crucial role in neurotransmitter synthesis and metabolism. Mutations in the PNPO gene, affecting PLP synthesis, can lead to neurological disorders, suggesting the importance of PLP in maintaining neurological health during aging. For instance, pyridoxine responsiveness in novel PNPO gene mutations was discussed as significant in neonatal epileptic encephalopathy cases (R).
Significant age-dependent changes in PLP synthesising enzymes were found in the hippocampal region of gerbils. This indicates that decreases in these enzymes might be involved in aging processes related to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) function (R).
A study on older men indicated that vitamin B6 supplementation (using pyridoxine HCl) could modestly but significantly improve memory, particularly long-term memory. This suggests that B6 vitamins might affect cognitive health during aging (R).