Summary
|
|
What is Magnesium Malate?
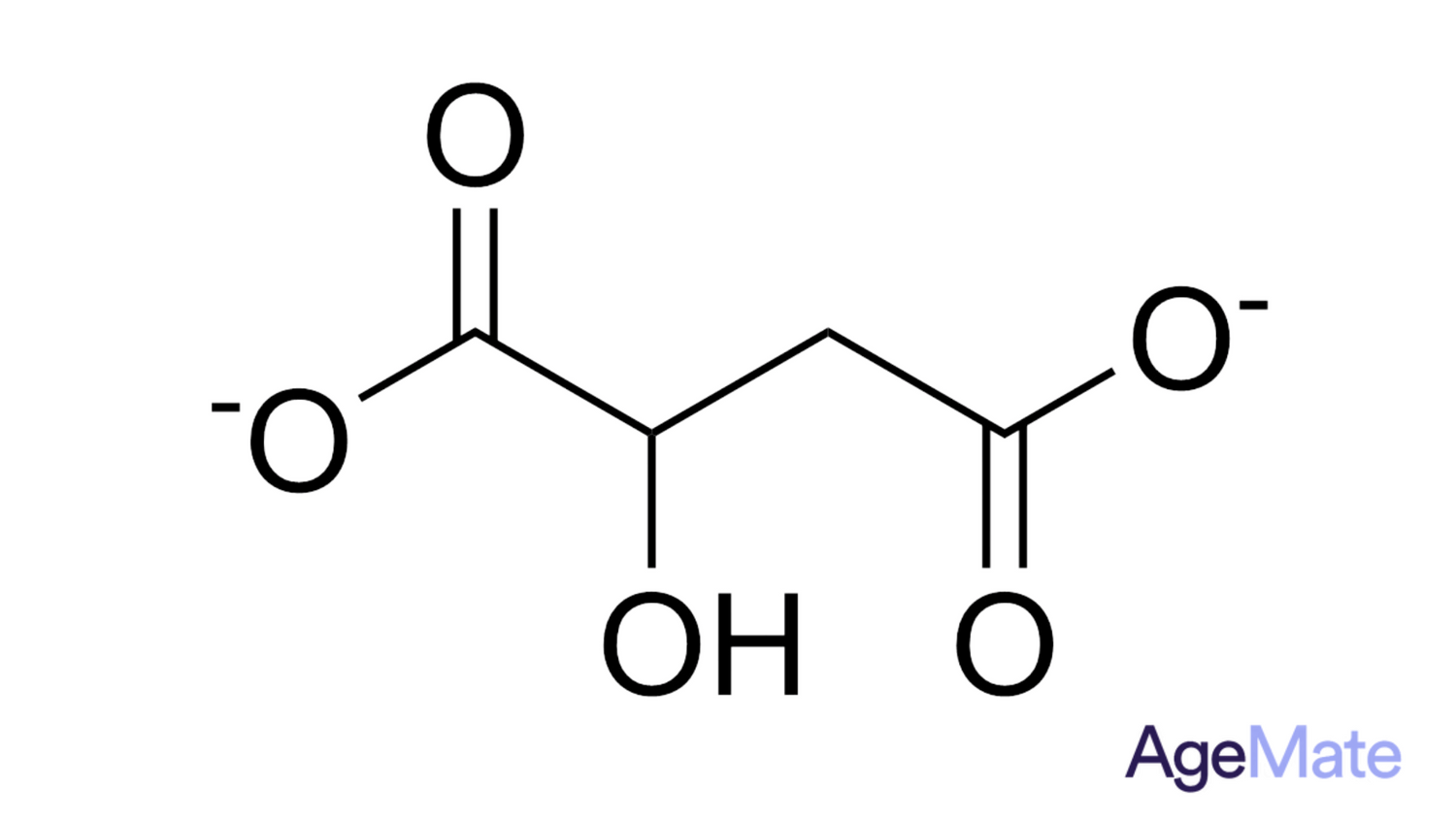
Magnesium malate, a dietary supplement, merges magnesium—a crucial mineral for bodily functions—with malic acid, commonly found in fruits like apples and plays a role in the Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle) within cells, contributing to energy production.
Magnesium Malate Impact on Aging
Maintaining adequate levels can help ease inflammation associated with accelerated aging (R).
Enhanced ATP generation and metabolism indirectly support cellular functions, potentially slowing age-related decline (R).
Magnesium malate may alleviate oxidative stress, a factor in age-related issues, potentially slowing aging (R).
Malate enhances vital antioxidant enzymes, combating aging-related free radicals and promoting overall health (R).
Magnesium malate supports cellular function through DNA stabilisation and promoting cell longevity, indirectly contributing to healthier aging (R).
Supporting heart function, regulating blood pressure, and contributing to bone density indirectly impact overall well-being and longevity (R).
Magnesium, Malate and Longevity Studies
Lifespan
Findings from this study suggest that various metabolites, including malate, can influence lifespan and stress response pathways in some organisms, providing insights into potential strategies for delaying age-related decline and improving health in old age (R, R).
Protects DNA
These studies show magnesium helps stabilise DNA in cells, promoting their longevity and genomic stability in yeast and human cells, whether used alone or during dietary calorie restriction (R, R).
A magnesium-dependent process prevents harmful RNA-DNA hybrids in genes. Missing key elements like yeast Pbp1 or human ATXN2 leads to gene instability. Calorie restriction or increased magnesium levels activate specific proteins, reducing gene instability in yeast and humans. Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 44, Issue 18, 14 October 2016, Pages 8870–8884,
Reduce Inflammation
In vitro studies demonstrate magnesium deficiency triggers an inflammatory response by increasing cellular calcium levels, activating leukocytes and macrophages, releasing pro-inflammatory cytokines, and elevating the production of free radicals. Free radicals are a key contributor to aging (R).
Reduce oxidative stress
Magnesium deficiency, common in many industrialised countries, may contribute to oxidative stress, cardiovascular diseases, and accelerated aging, making it a significant concern for overall health and well-being (R).
Enhance Antioxidant Activity
Malate can enhance antioxidant activity in elderly rats by augmenting crucial antioxidant enzymes like glutathione peroxidase and superoxide dismutase (R).